DeepSpeed ZeRO-3 Offload
Today we are announcing the release of ZeRO-3 Offload, a highly efficient and easy to use implementation of ZeRO Stage 3 and ZeRO Offload combined, geared towards our continued goal of democratizing AI by making efficient large-scale DL training available to everyone. The key benefits of ZeRO-3 Offload are:
- Unprecedented memory efficiency to run very large models on a limited number of GPU resources - e.g., fine-tune models with over 40B parameters on a single GPU and over 2 Trillion parameters on 512 GPUs!
- Extremely Easy to use:
- Scale to over a trillion parameters without the need to combine multiple parallelism techniques in complicated ways.
- For existing DeepSpeed users, turn on ZeRO-3 Offload with just a few flags in DeepSpeed Config file.
- High-performance per-GPU throughput and super-linear scalability across GPUs for distributed training.
- With 1 Trillion parameters, ZeRO-3 Offload sustains 25 PetaFlops in compute performance on 512 NVIDIA V100 GPUs, achieving 49 TFlops/GPU.
- Up to 2x improvement in throughput compared to ZeRO- 2 Offload on single GPU
Overview of ZeRO family of technology
The ZeRO Redundancy Optimizer (abbreviated ZeRO) is a family of memory optimization technologies for large-scale distributed deep learning. Unlike data parallelism (that is efficient but can only support a limited model size) or model parallelism (that can support larger model sizes but requires significant code refactoring while adding communication overhead that limits efficiency), ZeRO allows fitting larger models in memory without requiring code refactoring while remaining very efficient. ZeRO does so by eliminating the memory redundancy that is inherent in data parallelism while limiting the communication overhead to a minimum. ZeRO removes the memory redundancies across data-parallel processes by partitioning the three model states (optimizer states, gradients, and parameters) across data-parallel processes instead of replicating them. By doing this, it boosts memory efficiency compared to classic data-parallelism while retaining its computational granularity and communication efficiency. There are three stages in ZeRO corresponding to three model states, as shown in the Figure 1: the first stage (ZeRO-1) partitions only the optimizer states, the second stage (ZeRO-2) partitions both the optimizer states and the gradients and the final stage (ZeRO-3) partitions all three model states (for more details see the ZeRO paper).
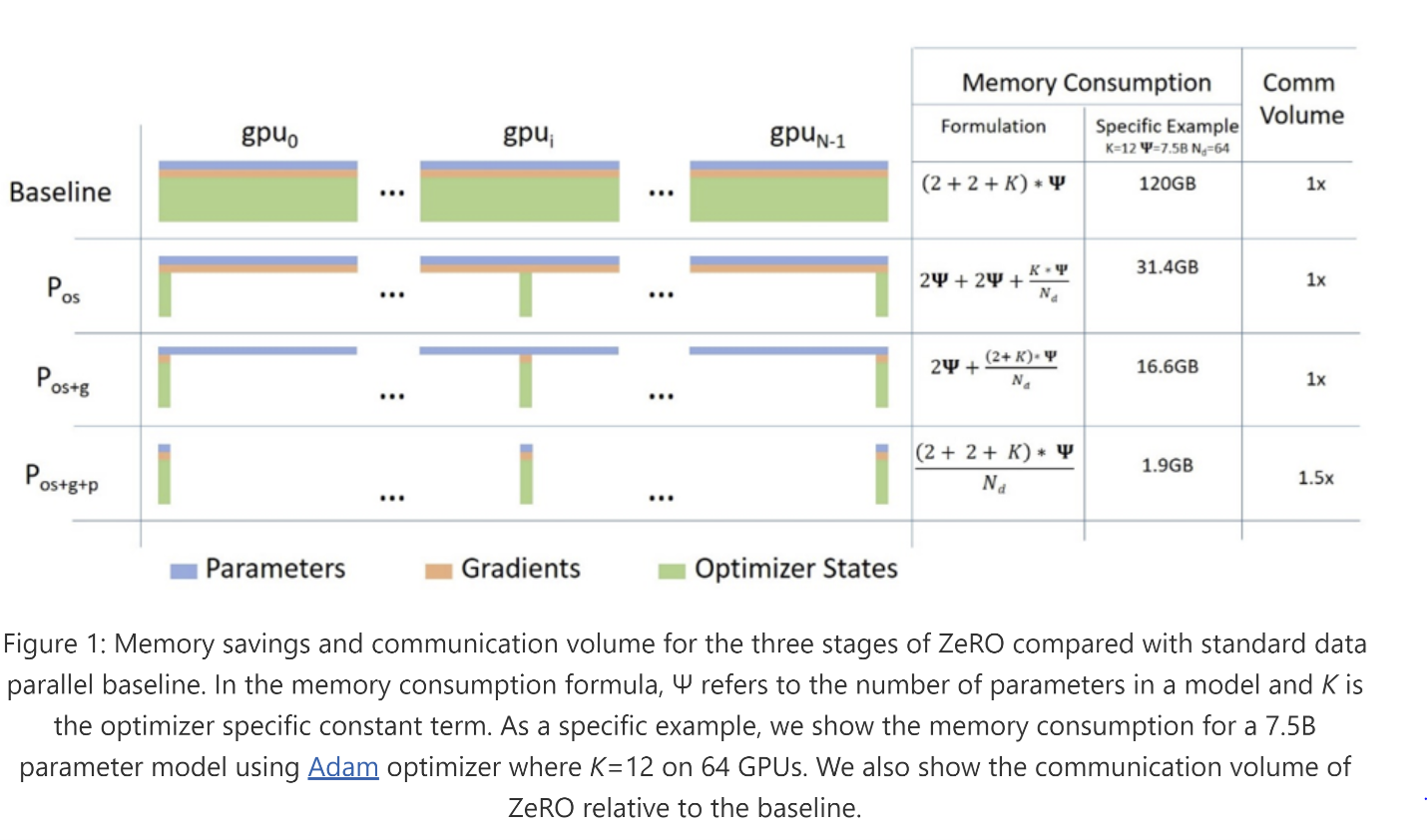 Figure 1. Overview of ZeRO memory savings
Figure 1. Overview of ZeRO memory savings
In addition to these three stages, ZeRO family of technology also consists of ZeRO-2 Offload. ZeRO-2 Offload is a heterogeneous DL training technology that works in conjunction with ZeRO-2 to offload partitioned optimizer states and gradients to CPU memory. ZeRO-2 Offload offers the full memory advantage of ZeRO-2 even on a single GPU, while at the same time offering great scalability of ZeRO-2 on multi-GPU setup. DeepSpeed library has been offering ZeRO-2 Offload since Sept 2020. For details, please see below:
- ZeRO: Stage 1 blog, Stage 2 blog, Tutorial
- ZeRO-Offload: Blog, Tutorials, Paper link
ZeRO-3 Offload
With today’s release of ZeRO-3 Offload, we are adding support for partitioning and offloading parameters in addition to optimizer states and gradients partitioning already supported by ZeRO-2 Offload in DeepSpeed. With parameter partitioning ZeRO-3 Offload implements the full set of features in the three stages of ZeRO, that allows for a linear growth in model size with the number of GPUs. In addition, ZeRO-3 Offload can also optionally offload all these model states to CPU to further reduce GPU memory consumption, leveraging both CPU and GPU to maximize memory and compute efficiency of the entire system.
We believe ZeRO-3 Offload offers a massive leap for large model training, in three regards:
i) Unprecedented model scale,
ii) Ease of supporting very-large models, and
iii) Achieving excellent training efficiency.
Unprecedented model scale
Unlike ZeRO-2 and ZeRO-Offload where the parameters have to fit in the memory of a single GPU, ZeRO-3 Offload can partition the parameters across GPUs, and offload them to CPU, supporting model sizes that are much larger than the memory on a single GPU. Furthermore, ZeRO-3 Offload goes beyond the state-of-the-art hybrid 3D-parallelism (data, model and pipeline parallelism combined). While 3D Parallelism is limited by the aggregate GPU memory, ZeRO-3 Offload can exploit both GPU and CPU memory, the latter of which is much larger and cheaper compared to GPU memory. This allows ZeRO-3 Offload to train larger model sizes with the given GPU and CPU resources than any other currently available technology.
Model Scale on Single GPU: ZeRO-3 Offload can train models with over 40B parameters efficiently on a single GPU (e.g., 32GB V100 GPU + 1.5TB CPU memory). This is 3x larger than what is possible with ZeRO-2 Offload, the current state-of-the art.
Model Scale on Multi-GPUs: With ZeRO-3 Offload you can train a trillion and two trillion parameter models on NVIDIA 32GB V100 DGX-2 cluster with 256 GPUs and 512 GPUs, respectively. In contrast, the state-of-art 3D Parallelism requires 800 GPUs, and 1600 GPUs, respectively, to fit the same sized models. This represents a 3x reduction in GPUs required to fit models with over a trillion parameters.
Ease of supporting very large models
From a system perspective, training models with hundreds of billions and trillions of parameters is extremely challenging. Data parallelism cannot scale the model size much further beyond a billion parameters, model parallelism (with tensor slicing) cannot be used to scale model size efficiently beyond a single node boundary due to massive communication overheads, and pipeline parallelism cannot scale beyond the number of layers available in a model, which limits both the model size and the number of GPUs that it can scale to.
The only existing parallel technology available that can scale to over a trillion parameters on massively parallel GPU clusters is the 3D parallelism that combines data, model and pipeline parallelism in complex ways. While such a system can be very efficient, it requires major model code refactoring from data scientists to split the model into load balanced pipeline stages. This also makes 3D parallelism inflexible in the type of models that it can support, since models with complex dependency graphs cannot be easily converted into a load balanced pipeline.
ZeRO-3 Offload address these challenges in two ways:
i) With ground-breaking memory efficiency, ZeRO-3 and ZeRO-3 Offload are the only DL parallel technology that can efficiently scale to over a trillion parameters by itself, without requiring a hybrid parallelism strategy, greatly simplifying the system stack for DL training.
ii) ZeRO-3 Offload requires virtually no model refactoring from model scientists, liberating data scientists to scale up complex models to hundreds of billions to trillions of parameters.
Excellent training efficiency
High-performance per-GPU throughput on multiple nodes: ZeRO-3 Offload offers excellent training efficiency for multi-billion and trillion parameter models on multiple nodes. It achieves a sustained throughput of up to 50 Tflops per GPU running on 32 DGX2 nodes comprising 512 NVIDIA V100 GPUs (see Figure 2). In comparison, the standard data parallel training with PyTorch can only achieve 30 TFlops per GPU for a 1.2B parameter model, the largest model that can be trained using data parallelism alone.
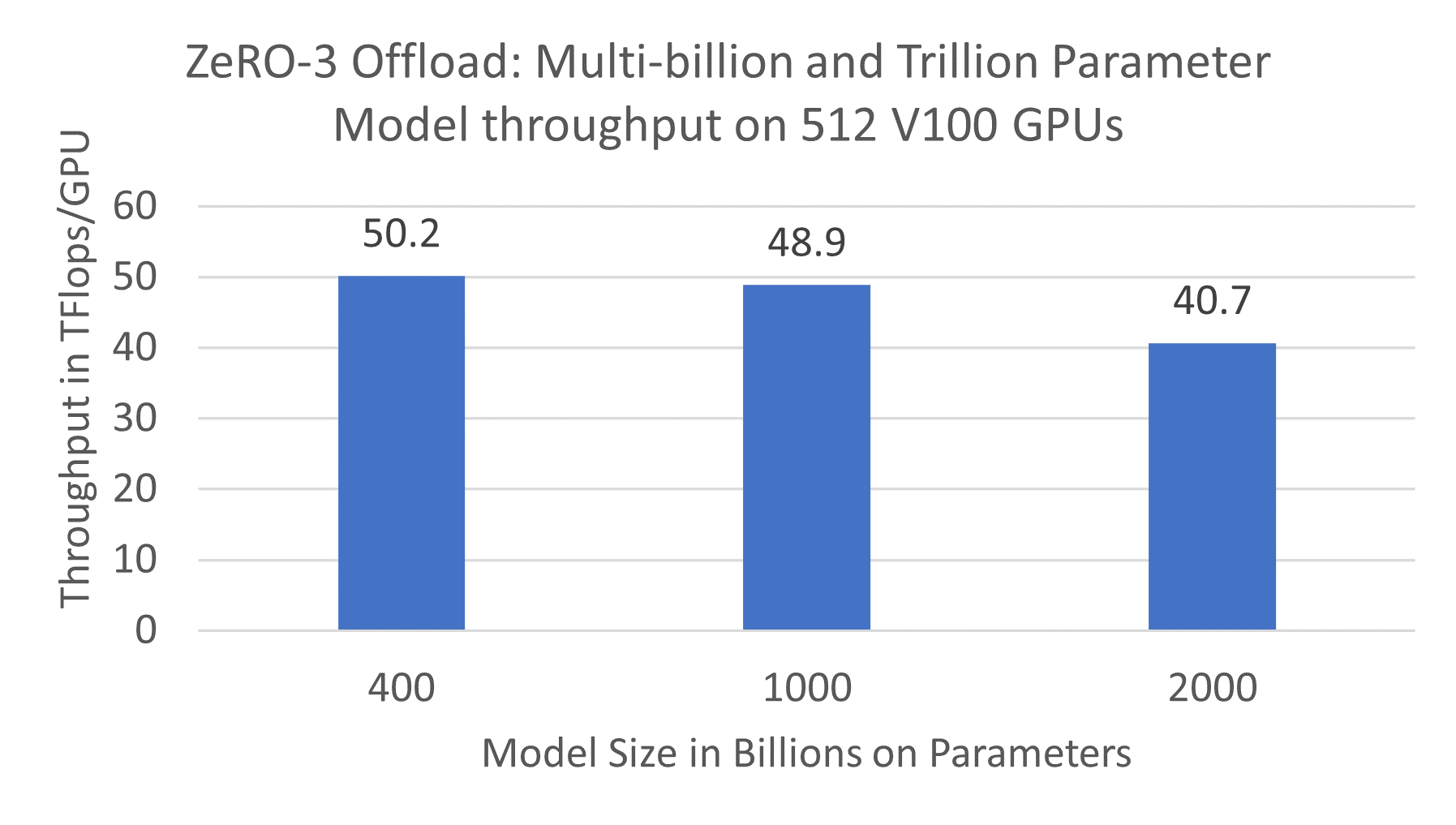 Figure 2. ZeRO-3 Offload: Multi-billion and trillion parameter model throughput on 512 V100 GPUs
Figure 2. ZeRO-3 Offload: Multi-billion and trillion parameter model throughput on 512 V100 GPUs
ZeRO-3 Offload obtains high efficiency despite the 50% communication overhead of ZeRO Stage 3 compared to standard data parallel training for a fixed batch size. This is made possible through a communication overlap centric design and implementation, which allows ZeRO-3 Offload to hide nearly all of the communication volume with computation, while taking advantage of a larger batch size for improved efficiency resulting from better GPU memory efficiency.
Efficient multi-billion parameter model training on a single GPU: ZeRO-3 Offload further democratizes AI by enabling efficient training of multi-billion parameter models on a single GPU. For single GPU training, ZeRO-3 Offload provides benefits over ZeRO-2 Offload along two dimensions. First, ZeRO-3 Offload increases the size of models trainable on a single V100 from 13B to 40B. Second, for ZeRO-3 Offload provides speedups (e.g., 2.3X for 13B) compared to ZeRO-2 Offload for model sizes trainable by both solutions. These results are summarized in Figure 3.
 Figure 3. Multi-billion parameter model training on one V100 GPU
Figure 3. Multi-billion parameter model training on one V100 GPU
Super-Linear scalability across GPUs: Additionally, ZeRO-3 Offload also preserves the super-linear scalability characteristics that we have demonstrated with all our previous ZeRO technologies (ZeRO Stage 1, ZeRO Stage 2 and ZeRO Offload). ZeRO-3 Offload can exploit the aggregate PCI-E bandwidth between GPU and CPU across all the GPUs in multi-GPU training configuration, and at the same time, it can also exploit the aggregate CPU compute across all the nodes. As a result, the CPU-GPU-CPU communication time as well as the optimizer update time decreases linearly with number of GPUs and nodes, respectively, allowing ZeRO-3 Offload to exhibit super-linear scaling (see Figure 4).
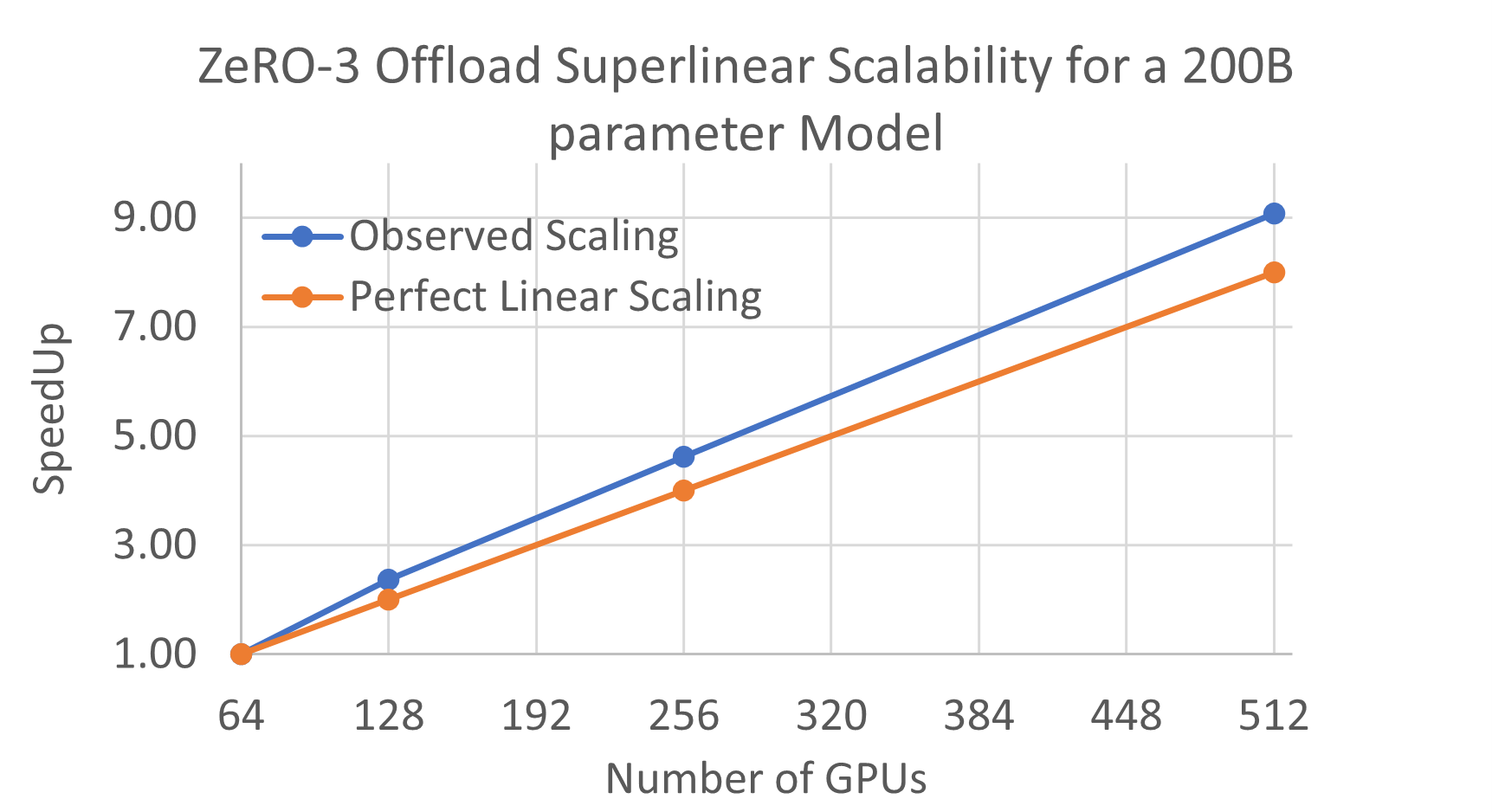 Figure 4. ZeRO-3 Offload Superlinear Scalability for a 200B parameter model.
Figure 4. ZeRO-3 Offload Superlinear Scalability for a 200B parameter model.
How to use ZeRO-3 Offload
As with many other existing DeepSpeed features, once the user model has been converted to use DeepSpeed, enabling ZeRO-3 Offload is as easy as turning on a couple of flags in DeepSpeed Config file. Supporting advanced features like weight sharing, or enabling extremely large models that requires to be partitioned across GPUs/nodes to fit in GPU/CPU memory, can be done with just a couple of additional lines of code change using the ZeRO-3 Offload API.
If you are already a DeepSpeed user, you can find our detailed tutorial on ZeRO-3 Offload below. If you are new to DeepSpeed, we recommend that you start at the getting started page before trying out our ZeRO-3 Offload Tutorial.
-
DeepSpeed: Getting Started Page
-
ZeRO-3 Offload Documentation, Tutorial
The DeepSpeed Team is very excited to share ZeRO-3 Offload with the DL community.